On the cover: Final results after segmentation by SegNet and HoughCNet followed by probabilistic Hough Line Transform on a sample Bean field image
This work is done at PixelFarmingRobotics BV. (client of CBoost BV. Inc.). The aim of the project is to produce a robust crop row detection pipeline that can extract crop rows from an image feed. This pipeline is then deployed and used on Pixie and Robot One to help in autonomous guided navigation on the field.
Due to the nature of the dataset and the usage of image processing techniques, the task poses several challenges:
- Weed infestation
- Various POVs (top view/ horizon view)
- Lighting/noise conditions
- Different growth stages of the crop (for segmentation)
The task of crop row detection can be divided into two sub-problems:
- Segmentation of crops (distinguish the crop from the soil and weed)
- Line Detection of the major crop rows (using the above segmentation results)
Two appraoches were considered for the whole task: OpenCV algorithms and Deep learning techniques. The pros and cons were considered for each technique and the best method was chosen for each sub-problem.
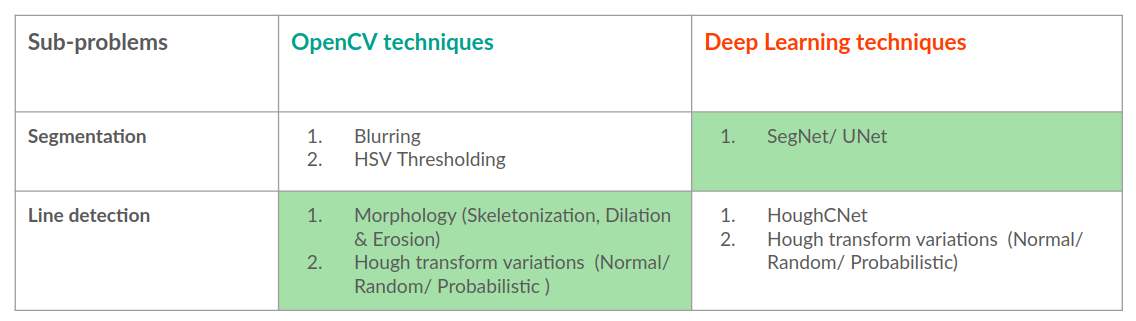 OpenCV and Deep Learning techniques for the sub-problems
OpenCV and Deep Learning techniques for the sub-problems
Data:
Data labeling is a huge bottleneck. Several open-source online annotation tools were considered for the task, but they lack the features of a paid tool and are poor/less supported or simply have less features. Even with open-source tools, we needed some additional pre-processing. Hence we adopted a preliminary HSV masking in OpenCV followed by weed removal manually in Gimp.
Two datasets were available for the project:
- Target data: TOGBeanField images (propreitary, aerial view, 72 images, no labels)
- For proof of concept: Weedmap An open source data of a maize field (aerial view, 176 images, labels available)
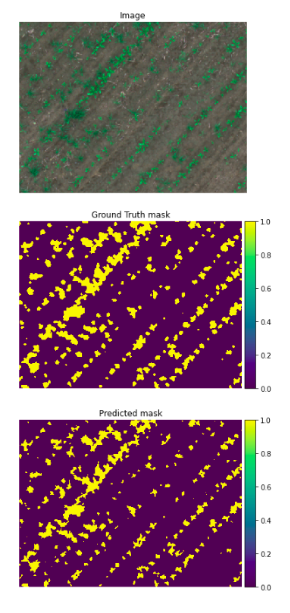 Segmentation result of SegNet on Weedmap data
Segmentation result of SegNet on Weedmap data
The results were promising on TOGBeanField with an IOU score of 0.87 by applying both SegNet and HoughCNet in succession and taking an intersection of the predicted areas. The ML code was written in PyTorch Lightning, trained using an augmented dataset and tested on part of the dataset (10%). The trained model was then deployed on the robot as a codelet in Isaac 2020.2 on the Jetson Xavier AGX and at inference uses TensorRT to increase performance.
Further project details and code base are not revealed since the work is under NDA
