On the cover: Pioneer 3Dx as base, CoolArm1000 7DoF and a mounted kinect sensor
Robots operating in real-world environments can be expected to come across objects that they have never encountered before, but nevertheless, have to make use of for fullfilling their goals. One approach to operating in such a fashion is for the robots to have the capability to learn how to use novel objects, or in other words, learn object affordances. These affordances can then be used in the planning (and execution) process to achieve the required goals.
Thus, the aim of this research project is to come up with affordance learning schemes that allow agents to autonomously acquire skills (in terms of the ability to interact with novel objects/in novel situations) commensurate with their capabilities and demonstrate the use of such learning schemes in solving problems in the domain of open world planning.
We explore two main capabilities of the robot using ROS framework and build the behaviour repertoire of the robot:
-
Moveit_stack: Given the characteristics of the target object, the capability of the robotic arm to find a collision-free path to grasp that object and execute it through inverse kinematics using inbuilt controllers which are inherent to the robotic arm.
-
Navigation_stack: Given an arena and a goal point, the capability of the robot to build a costmap using the already built/existing static map or by dynamically mapping the environment and to navigate to the goal without running into any obstacles in its path.
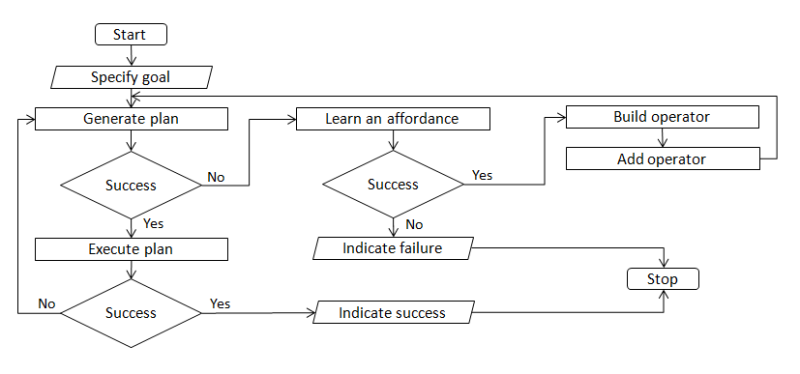 Control flow diagram for planning, affordance learning and action model learning
Control flow diagram for planning, affordance learning and action model learning
Simulation using Gazebo: Constructed Xacro files (converted to URDF) as robot descriptors importing all the designed meshes of robotic components. Gazebo ROS Differential drive plugin is included to make the robot a differential drive. In-built gazebo plugins are added to specify the function of on-board sensors: LiDAR, IMU, encoders and camera. Other capabilities such as teleop and controller interfaces are included while building the robot on the simulator.
This includes the RL part of the project:
Planning component - Backward Search Affordance learning component - Intrinsically Motivated Reinforcement Learning (IMRL) Action model learning component - 3SG (Simultaneous Specification, Simplification, and Generalisation)
Backward search is a relatively simple state space search algorithm and we have implemented it in a classical planning setting. With the use of this heuristic, we can provide the affordance learning component (IMRL) of our approach with useful information to guide its search process (in the case of plan failure). In order to be able to make use of the newly acquired affordance skills in the planning process, an action model learning component (3SG) is being implemented.
